Core Data is a powerful mobile database allowing developers to create high performance, data-driven iOS and macOS applications. This post presents examples of creating, updating, and deleting Core Data objects in Swift:
- Defining A New Core Data Entity
a. New Data Model Entity Using Xcode
b. Xcode NSManagedObject Sync - Create A New Core Data Object
a. New NSManagedObject Example
b. Use of unresolved identifier ‘Entity’
c. Command CompileSwiftSources failed with a nonzero exit code - Update A Core Data Object
- Delete A Core Data Object
Note: Object manipulation in Core Data requires an NSManagedObjectContext. The examples in this post assume the variable context is in scope and is a NSManagedObjectContext.
Defining A New Core Data Entity
Core Data is well integrated in Xcode, providing a visual interface for definition entities, properties, and relationships. To open the Data Model Editor, select a .xcdatamodeld file:
New Data Model Entity Using Xcode
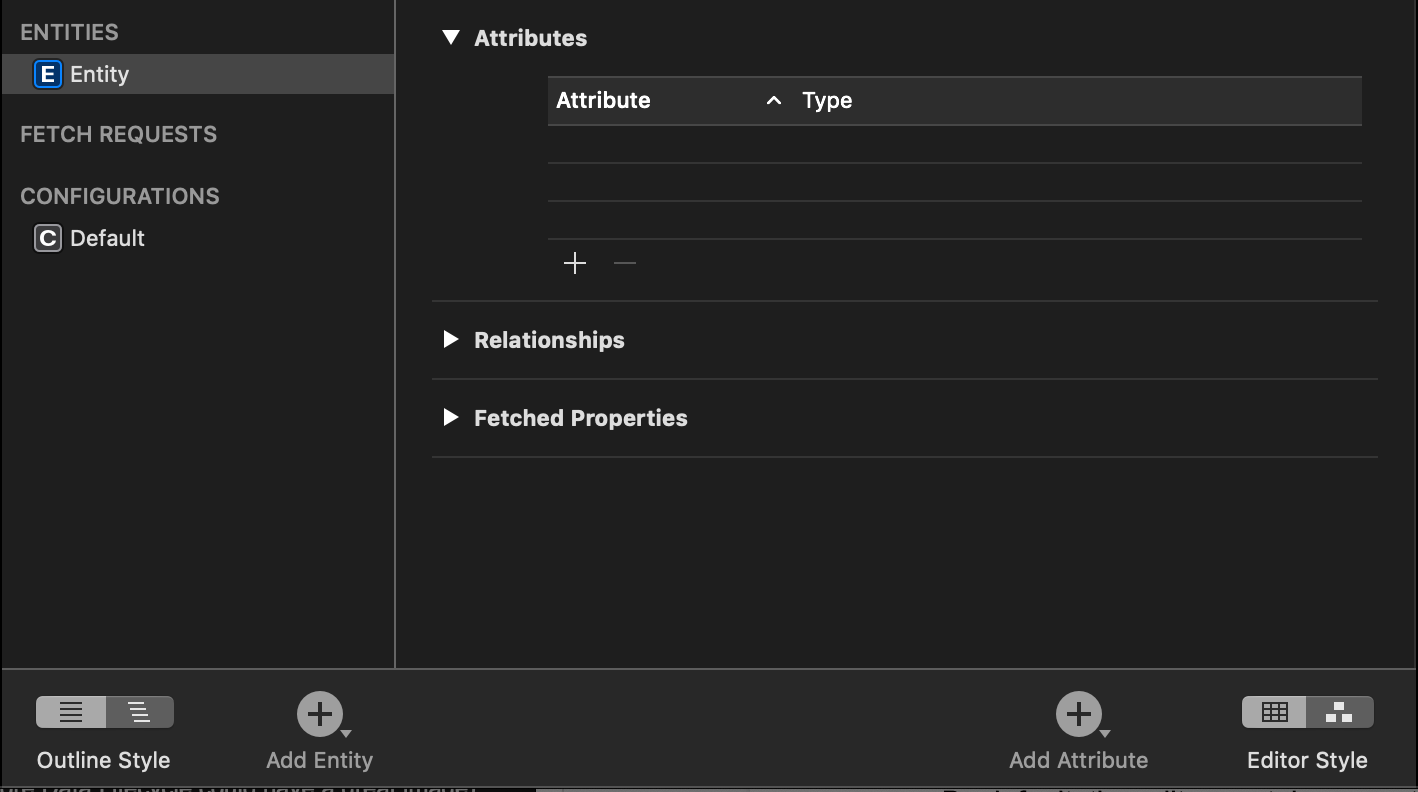
By default, the editor contains no entities. Select Add Entity in the lower left to create a new entity called Entity with no properties:
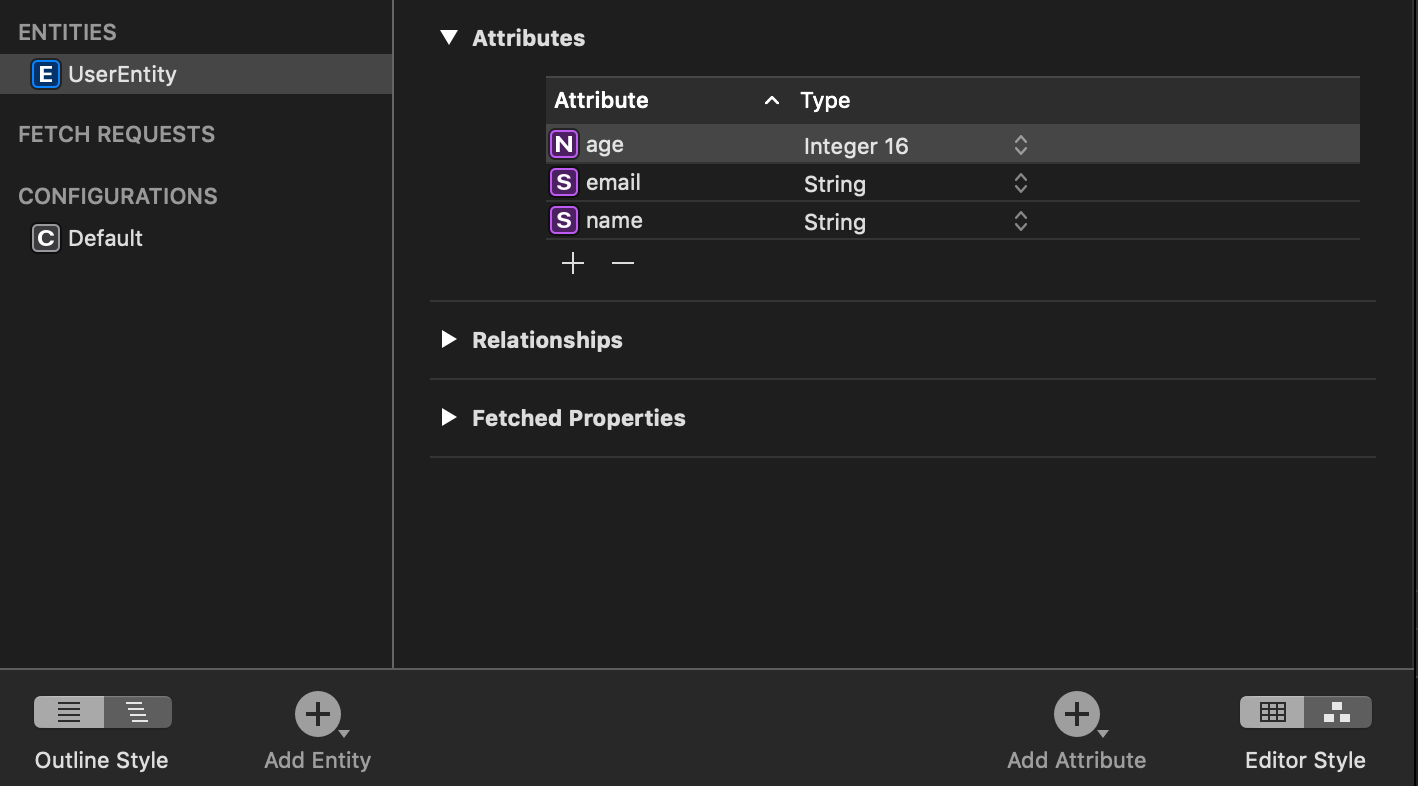
Double clicking on the name Entity allows a more descriptive name to be entered. In this example the entity was renamed UserEntity.
Properties of UserEntity can be added by using the plus button under the Attributes table. For this example, three properties were created. A property age of type Int16, email of type String, and name of type String:
Xcode automatically saves changes to the .xcdatamodeld file when using the visual Data Model Editor.
Xcode NSManagedObject Sync
Defining entities in the .xcdatamodeld file enables Xcode to create types automatically for each entity. In this example, when the project is built Xcode will use the UserEntity definition in the .xcdatamodeld file to create a UserEntity type available in Swift.
This UserEntity type will automatically have the same properties as the entity definition in the .xcdatamodeld file. Specifically, the UserEntity type will have a Int16 property age, a String? property email, and a String? property name.
Create A New Core Data Object
After defining a new UserEntity entity in the .xcdatamodeld file, UserEntity can be used as a type in Swift. The UserEntity constructor takes in a NSManagedObjectContext and returns an instance of UserEntity with all properties set to default values.
New NSManagedObject Example
// Create a new UserEntity in the
// NSManagedObjectContext context
let user = UserEntity(context: context)
// Assign values to the entity's properties
user.name = "User Name"
user.email = "user@domain.com"
user.age = 32
// To save the new entity to the persistent store, call
// save on the context
do {
try context.save()
}
catch {
// Handle Error
}Use of unresolved identifier ‘Entity’
One common error when working with Xcode managed .xcdatamodeld file is Use of unresolved identifier 'Entity'. This error means that Xcode did not properly update entity description changes in the .xcdatamodeld when compiling the iOS or macOS application.
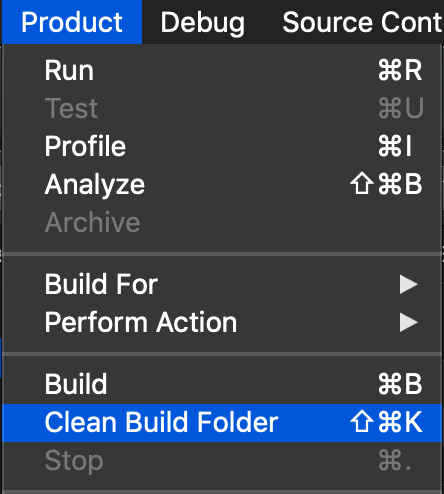
Cleaning the build folder can often resolve this issue. The build folder can be cleaned using the Product menu and selecting Clean Build Folder:
Command CompileSwiftSources failed with a nonzero exit code
Another common error when working with Xcode managed .xcdatamodeld file is Command CompileSwiftSources failed with a nonzero exit code and is often preceded with error: no such file or directory.
Like the Use of unresolved identifier error, cleaning the build folder can often resolve this issue.
Update A Core Data Object
// Update entity properties as needed
user.age = 33
// To save new entity updates to the persistent store,
// call save on the context
do {
try context.save()
}
catch {
// Handle Error
}
Delete A Core Data Object
// Delete the entity from the context
context.delete(user)
// To delete the entity from the persistent store, call
// save on the context
do {
try context.save()
}
catch {
// Handle Error
}
Saving, Modifying, and Removing An NSManagedObject in Swift
That’s it! By using NSManagedObject, NSManagedObjectContext, and Xcode, you can define new database entities, create new entities, update existing entities, and delete entities in Swift.